Charging guide
Electric vehicle (EV) charging is a new concept to all first time EV owners. It is not quite as simple as filling up with petrol; charging speeds, connector types, and understanding your vehicle specification, are all important considerations. But don’t worry, we’ve created a series of simple guides to explain the world of EV charging.
These guides will help to explain the ins and outs of charging on public networks, charging at home, charging at work, as well as some of the more detailed points around EV charging in general.
To find a charging point near you using [http://www.zap-map.com/live/]Zap Map [https://www.zap-map.com/live/]
EV charging explained
EV chargers are classed as rapid or ultra-rapid, fast and slow or standard, depending on their speed.
- Low speed and Standard – often used at residential properties and on residential streets, including lamppost column charging.
- Standard and Fast – this is the power of chargepoint often used in residential or destination areas, including public car parks.
- Rapid and Ultra Rapid – these are often installed in short stay areas, such as petrol stations or Motorway Service Areas. These are also often useful for electric taxi recharging.
| Use | Referred to | AC | DC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long stay home, work or destination charging | Slow | Under 3.5kW | |
| Standard | 3.5kW to 7kW | ||
| Fast | 7kW to 23kW | 10kW to 22kW | |
| Short stay on-route, or opportunity charging | Semi-rapid | 43kW to 44kW | 22kW to 50kW |
| Rapid | 50kW to 62.5kW | ||
| Ultra-rapid | 62.5kW to 500kW |
Electric vehicles and charging
How to charge your electric vehicle
The majority of charging your vehicle will be done at home, usually overnight. If you have a driveway or garage, the cheapest and most convenient way is to install a dedicated chargepoint.
Charging an electric vehicle at home
The Office for Zero Emission Vehicles (OZEV)’s EV chargepoint grant, is available to owner/occupiers of flats and renters of residential property with off-street parking. Landlords can apply for the EV chargepoint grant for landlords. Both of these cover up to 75% of the costs of installing a home chargepoint, up to a limit of £350. Also available for private or social landlords is the EV infrastructure grant for residential car parks that can help fund the installation of cabling for EV chargepoints.
For more details on the grants available see OZEV electric vehicle [https://www.gov.uk/guidance/electric-vehicle-chargepoint-and-infrastucture-grant-guidance-for-installers#grants-that-are-available-to-your-customers]chargepoint and infrastructure grants [https://www.gov.uk/guidance/electric-vehicle-chargepoint-and-infrastucture-grant-guidance-for-installers#ev-chargepoint-grant] [https://www.gov.uk/guidance/electric-vehicle-chargepoint-and-infrastucture-grant-guidance-for-installers#grants-that-are-available-to-your-customers]
While you can use a regular UK three-pin socket, it is much slower than a dedicated chargepoint and may involve running charging cables from inside your home. These cables do not have as many safety features as a type 2 cable, and should not be used as a long-term solution for home charging.
Don’t have access to off-street parking? Coventry has deployed a network of on-street residential charging stations.
Charging at work
It is highly convenient to charge at work, because, much like charging at home, your car is often parked for an extended period during the day.
Many organisations are now installing charging stations for staff and visitors as a perk, for sustainability reasons or to facilitate the switch to an electric fleet.
To help towards the cost of installing an EV chargepoint socket at your workplace, the following grants are available
- Chargepoint and infrastructure grant for business staff and fleet car parks [https://www.find-government-grants.service.gov.uk/grants/electric-vehicle-infrastructure-grant-for-staff-and-fleets-1]
- Workplace Charging Scheme [https://www.find-government-grants.service.gov.uk/grants/workplace-charging-scheme-2]
The EV infrastructure grant for staff and fleets, helps small and medium sized businesses install the infrastructure they need for chargepoints.
Electric vehicles and charging
Connectors and cables
There are two primary electric vehicle charging methods: AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current). All home EV chargers and the majority of public charging stations use AC, while DC is used for rapid charging.
AC connectors
- UK 3-pin (BS 1363)
- Industrial Commando (IEC 60309)
- American Type 1 (SAE J1772)
- European Type 2 (Mennekes, IEC 62196)
DC connectors
- Japanese JEVS (CHAdeMO)
- European Combined Charging System (CCS or ‘Combo’)
How do I choose a charging cable?
To charge your electric vehicle, you’ll need the correct charging connector. You need a charging cable with connectors that are compatible with both your car and the charging point you want to use.
If your vehicle does not come with the cable you need to charge it at home, at work, or in public, make sure that you understand the connector type that your vehicle is compatible with.
Most EVs will accept either a type 1 (typically older cars) or type 2 (the new European standard) connector and your manufacturer should be able to advise if you’re not sure which one you have.
While your car may also have a CHAdeMO or CCS compatible inlet for rapid charging, charging points with the corresponding connectors are usually only found at public fast charging stations. These connectors will usually be inbuilt, so it’s rare that you’d need to supply your own charging cable.
Can you charge an electric car from a three-pin plug?
Yes, but we’d advise against it. Three-pin domestic plugs are slow to charge, aren’t designed to handle high charging loads and aren’t designed to be a long-term charging solution (it wouldn’t be safe to use them all the time).
Electric vehicles and charging
Connector types
EV chargers are classed as rapid or ultra-rapid, fast and slow or standard, depending on their speed. This section will explain the different electric car plug types, EV connector types and charging cables, helping you identify which one you need.
Rapid and ultra-rapid chargers
Rapid chargers
- 50kW - 350kW DC charging with CHAdeMO or CCS
- All rapid units have tethered cables
| Type | Design |
|---|---|
| CHAdeMO 50 kW DC | 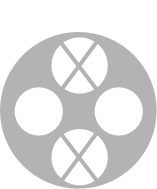 |
| CCS 50 kW DC |  |
DC Rapid chargers are the fastest way to charge an EV and are often found in motorway services or as part of a public network. DC Rapid chargers currently range from 50kW up to 350kW, with the capability to deliver between 180 and 1,200 miles of charge each hour. It is important to remember that most vehicles will start charging at a lower rate when the battery reaches around 80%, to protect the battery and extend its life. All rapid devices have the charging cable tethered to the unit.
Rapid charging can only be used on vehicles with rapid-charging capability.
Currently available rapid DC chargers provide power at between 50kW and 150kW and use either the CHAdeMO or CCS charging standards.
Ultra-rapid DC chargers can charge an EV battery even faster. Typically rated at 100kW upwards, 350kW chargers are starting to appear in the UK. Ultra-rapid chargers can refill an EV battery to 80% in around 20 minutes.
Fast chargers
- 7kW fast charging on one of three connector types
- 22kW fast charging on one of three connector types
- Units are either untethered or have tethered cables
| Type | Design |
|---|---|
| Type 2 – 7-22 kW AC | 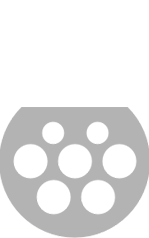 |
| Type 1 - 7 kW AC | 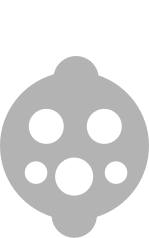 |
| Commando – 7-22 kW AC | 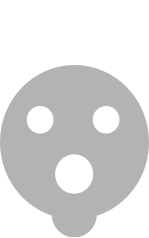 |
Fast chargers, all of which are AC, are typically rated at either 7 kW (32A, single-phase) or 22 kW (32A, three-phase). Charging times vary depending on the vehicle, but a 7 kW charger will recharge a compatible EV with a 30 kWh battery in 3-5 hours, and 1-2 hours for a 22 kW charger.
Charging rates when using a fast charger will depend on the car’s on-board charger, with not all models able to accept 7 kW or more. These models can still be plugged in to the charge point, but will only draw the maximum power accepted by the on-board charger. For example, a Nissan Leaf with standard 3.3 kW on-board charger will only draw a maximum of 3.3 kW, even if the fast charger is 7 kW or 22 kW.
The majority of fast chargers are 7 kW and untethered, though some home and workplace based units have cables attached. The latter units mean only those vehicles that can use that connector will be able to charge on them; in contrast to the more common use of a driver’s own connector cable. Untethered units are therefore more flexible and can be used by any EV with their own cable.
Slow chargers
- 3kW slow charging on one of four connector types
- Charging units are either untethered or have tethered cables
- Includes mains charging and from specialist chargers
- Often covers home charging
| Type | Design |
|---|---|
| 3-Pin - 3kW AC | 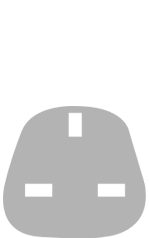 |
| Type 1 - 3 kW AC | 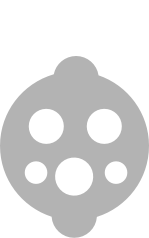 |
| Type 2 - 3 kW AC | 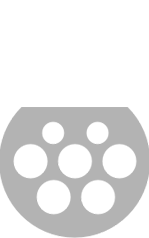 |
| Commando – 3 kW AC | 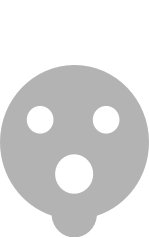 |
Most slow charging units are rated up to 3kW with some lamp-post chargers being rated at 6kW. Charging times vary depending on the charging unit and EV being charged, but a full charge on a 3 kW unit will typically take 6-12 hours. Most slow charging units are usually untethered, meaning that a cable is required to connect the EV with the charge point.
Slow charging is a very common method of charging electric vehicles, used by many owners to charge at home overnight. Slow units can also be found at workplaces and on public networks where the available electrical supply is not sufficient to accommodate fast units.
While slow charging can be carried out using a domestic 3-pin socket, because of the higher current demands of EVs and the duration spent charging, it is strongly recommended that those who need to charge regularly at home or the workplace get a dedicated EV charging unit installed by an accredited installer.
All plug-in EVs can charge using at least one of the above slow connectors using the appropriate cable. Most home units have the same Type 2 cable as found on public chargers, however some may require a Type 1 connector.
Electric vehicles and charging
Electric Vehicle charging network
ESB Energy: Rapid Charge Point network
There are 39 rapid chargers across Coventry. Find your nearest rapid charge point: Live and interactive charge point map (esbenergy.co.uk) [https://www.esbenergy.co.uk/ev/charge-points]
Rapid chargers can re-charge an electric vehicle in as little as 30 minutes using 100% renewable electricity. Customers can sign up to PAYG, Membership or Taxi price plans.
ESB Energy can be contacted on:
- Webpage: esbenergy.co.uk [http://esbenergy.co.uk]
- 24/7 phone support: 0345 609 0372
- Email: Evsupport@esbenergy.co.uk [mailto:Evsupport@esbenergy.co.uk]
- X: @ESBEVSolutions [https://www.twitter.com/@ESBEVSolutions]
- App: esbenergy.co.uk/ev/ev-app [https://esbenergy.co.uk/ev/ev-app]
Char.gy: Slow and Standard Charge point network
There are 373 slow and standard residential charge points provided by Char.gy across Coventry. Find your nearest Char.gy charge point [https://char.gy/map].
Char.gy can be contacted on:
- Webpage: char.gy website [http://char.gy]
- 24/7 helpline: 0800 086 9606 [tel:08000869606]
- Email: support@char.gy [mailto:support@char.gy]
- App: char.gy [https://char.gy/]
- X: @char_gy [https://x.com/char_gy]
Connected Kerb Ltd: Standard Charge point network
There are 160 standard residential charging sockets provided by Connected Kerb across Coventry. Find your nearest Connected Kerb charging socket [https://connectedkerb.com/charge-your-car/find-a-charging-point/].
Connected Kerb can be contacted on:
- Webpage: connectedkerb.com [https://connectedkerb.com]
- Helpline on 0800 0291 696 [tel:08000291696]
- Email: support@connectedkerb.co.uk [http://support@connectedkerb.co.uk]
- App: connectedkerb.com/our-technology/software/our-app/ [http://connectedkerb.com/our-technology/software/our-app/]
- X:@ConnectedKerb [https://x.com/@ConnectedKerb ]
For more information on everything EV, visit Zap Map [https://www.zap-map.com/].
E.ON EV chargers
There are 4 standard and 2 semi-rapid chargers available under E.ON. Find your nearest E.ON charging points [https://www.zap-map.com/live/].
E.ON can be contacted on:
- Webpage: eonnext.com/electric-vehicles/electric-vehicle-charger-support [https://eonnext.com/electric-vehicles/electric-vehicle-charger-support]
- Helpline on 0808 501 5088 [tel:+448085015088]
- Email: hi@eonnext.com [mailto:hi@eonnext.com]
- App: E.ON Drive Comfort App [https://www.eonnext.com/electric-vehicles/drive-comfort]
- Zapmap [https://www.zap-map.com/]
- X: @eonenergyuk [https://x.com/eonenergyuk]
For more information on everything EV, visit [http://www.zap-map.com/]Zap Map [https://www.zap-map.com/].

